A Game-Theoretical Approach for User Allocation in Edge Computing Environment
Nash equilibrium:一个博弈论概念。在 Nash equilibrium 情形中,每个玩家都不能在仅改变自己的策略(其他玩家策略不变)的情形下获得比平衡策略更高的收益。也就是一种平衡状态。例如,假设有 A,B,C,D 四个玩家达成了 Nash equilibrium,则在 B、C、D 的策略不变的前提下,A 无法通过改变自己的策略获得更优的收益,即 A 当前的策略就是最优的;且 B、C、D 同理。
Edge User Allocation (EUA) problem:通常一个用户会在多个 edge server 的覆盖区域中,所以需要指定该用户具体分配到哪个 edge server
这篇论文干了什么:
- 证明 EUA problem 是 NP-hard 的
- 将 EUA problem 转化为博弈论问题 EUA game
- 证明 EUA game 能达到 Nash equilibrium
- 提出使 EUA game 达到 Nash equilibrium 的非中心算法
数学模型
数学符号:
multi-tenancy benefits
(假设)单个 edge server 的 benefit(系数):
其中
user benefit
system cost
Optimization Model
形式化地表示 EUA problem:
限制条件为:
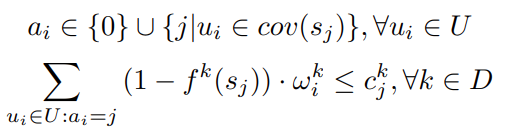
NP hardness
EUA problem 是 bin packing problem 的复杂形式。
bin packing problem 指的是将 n 个物品
,大小为 装到若干个大小为 的集装箱中,要求每个集装箱中的物品的大小之和不能超过 . 求最小需要几个集装箱. 这是一个 NP-hard 问题.
所以 EUA problem 是 NP-hard 问题。
EUA Game
利用博弈论的原因:
- 应用用户可能有不同的需求,博弈论适合用来设计激励相容的EUA机制
- EUA Game 使用分布式的解决方案,减少中心方案中服务器的压力,也有利于大规模应用
- 延时低
Game Formulation
设
EUA game 是否至少存在一种 Nash equilibrium 很重要
Potential Game:
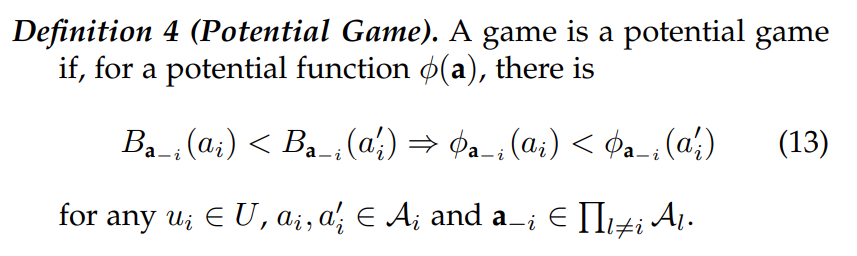
当一个 game 是 potential game 的时候,只需要找到 potential function
Individual Capacity Constraint
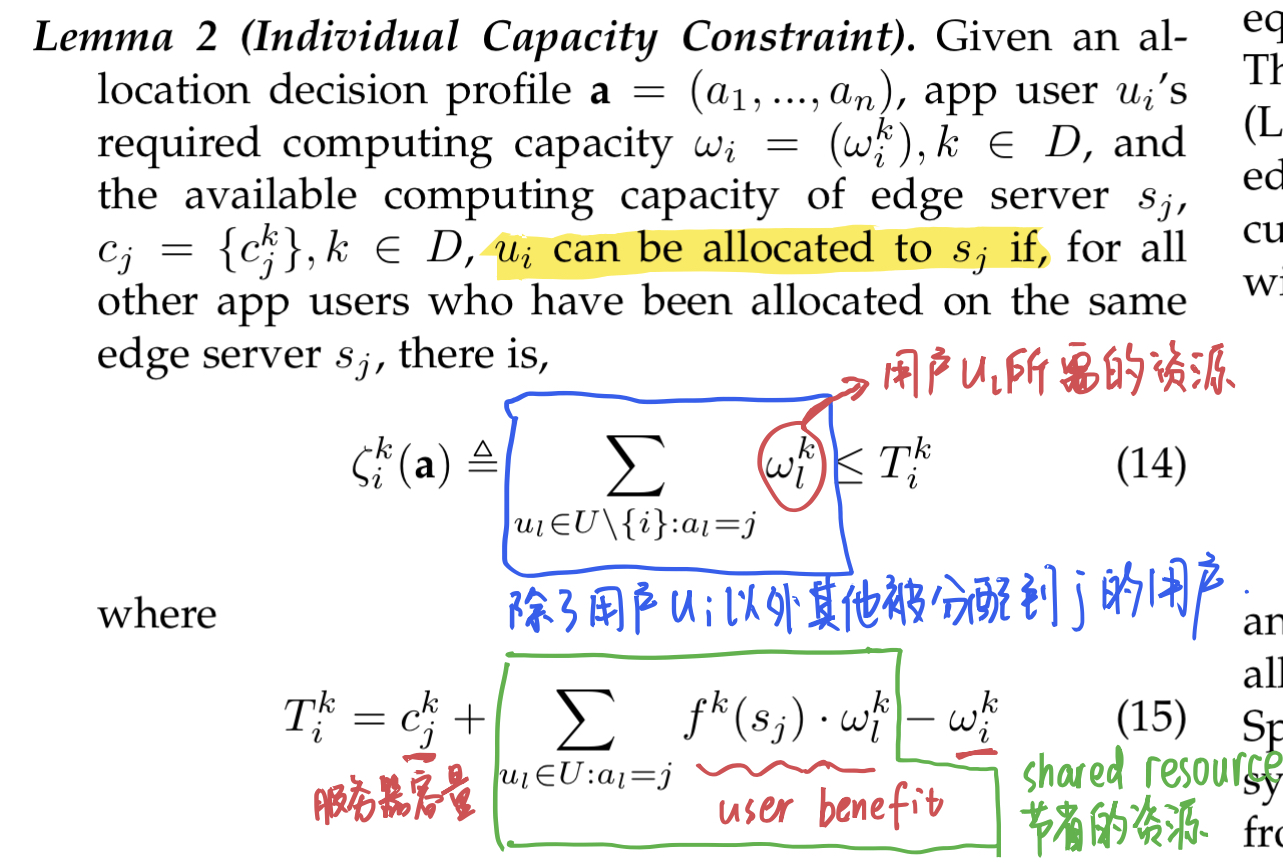

从证明中可以看出,
定义
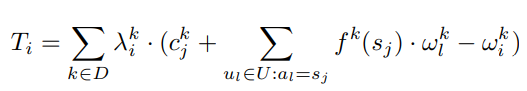
根据式(15),越多的用户被分配到同一个服务器会产生更多的 multi-tenancy benefits. 在此基础上,给出 EUA game 的 potential function:
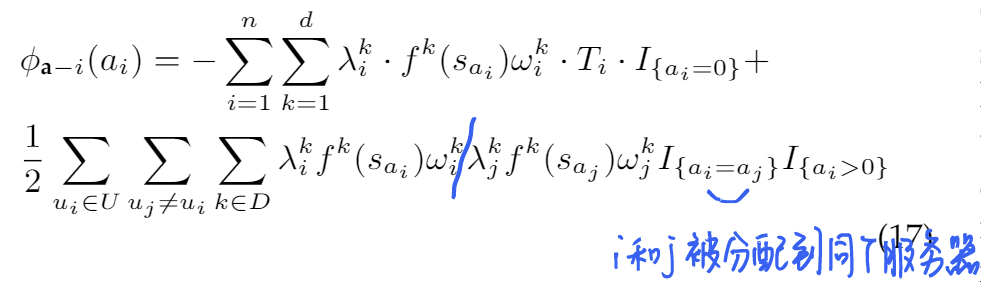
,也就是用户 没有被分配到 edge server,此时给出惩罚项 也就是用户 和 被分配到同一个 edge server,此时给出奖励项
Algorithm
algorithm 很简单,就是枚举用户

Theory Evaluation
提出 algorithm 后,论文用了 PoA 来衡量算法的表现。这里 PoA 定义为:
因为 EUA game 有两个评价指标:最大化分配成功的用户数、最小化 system cost,所以有两个对应的
显然,
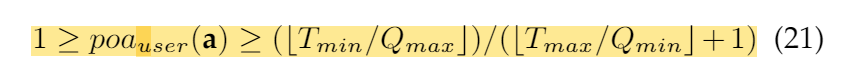
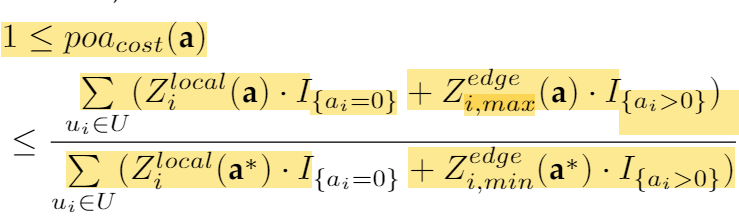
Experimental Evalutaion
比较对象:
- COP model 的最优化算法
- (baseline)Random:随机分配用户
- (baseline)Greedy:分配用户到资源最丰富的 edge server
实验数据来源:
- edge server 的位置取澳大利亚官方公布的基站数据集
- user 的位置通过分配给澳大利亚的 IP 地址,根据 IP 地址推断用户实际位置
- edge server 的覆盖位置取决于其周围的用户密度(用户密度越大,单个 edge server 的覆盖范围越小)
Related Work
给出了本文的创新点:从 app 供应商(而不是用户和服务器商)的角度解决 EUA 问题。
【?】所以这篇论文和 Efficient Multi-User Computation Offloading for Mobile-Edge Cloud Computing 的区别在于?
一个是 edge server 的角度,一个是 app vendor 的角度?这两个角度有什么不同?
我感觉就是 app vendor 的角度是分配用户到服务器,而 edge server 的角度是在服务器之间分配资源。换句话说,app vendor 无法控制服务器之间的通信?(个人理解qwq
Efficient Multi-User Computation Offloading for Mobile-Edge Cloud Computing做的是计算卸载,A Game-Theoretical Approach for User Allocation in Edge Computing Environment做的是用户分配。两篇文章都采用了相似的博弈论来解决问题。Efficient Multi-User Computation Offloading for Mobile-Edge Cloud Computing做的是计算卸载,A Game-Theoretical Approach for User Allocation in Edge Computing Environment做的是用户分配。两篇文章都采用了相似的博弈论来解决问题。
Efficient Multi-User Computation Offloading for Mobile-Edge Cloud Computing
Mobile-edge cloud computing is a new paradigm to provide cloud computing capabilities at the edge of pervasive radio access networks in close proximity to mobile users. In this paper, we first study the multi-user computation offloading problem for mobile-edge cloud computing in a multi-channel wireless interference environment. We show that it is NP-hard to compute a centralized optimal solution, and hence adopt a game theoretic approach for achieving efficient computation offloading in a distributed manner. We formulate the distributed computation offloading decision making problem among mobile device users as a multi-user computation offloading game. We analyze the structural property of the game and show that the game admits a Nash equilibrium and possesses the finite improvement property. We then design a distributed computation offloading algorithm that can achieve a Nash equilibrium, derive the upper bound of the convergence time, and quantify its efficiency ratio over the centralized optimal solutions in terms of two important performance metrics. We further extend our study to the scenario of multi-user computation offloading in the multi-channel wireless contention environment. Numerical results corroborate that the proposed algorithm can achieve superior computation offloading performance and scale well as the user size increases.